Bioinformatic Analysis of MicroRNA Sequencing Data
- 24th May 2024
- Posted by: Breige McBride
- Categories: Bioinformatics, Sequencing
As regulators of gene expression, microRNAs (miRNAs) influence many biological processes. This is why miRNA sequencing data is so valuable to researchers, as it helps to unravel the biological complexity encoded by our genomes. However, unravelling those complexities also requires bioinformatic analysis. Although microRNA sequencing data holds many genomic insights, bioinformatic analysis is necessary to translate those insights and make them available to researchers.
What is the Role of Bioinformatics in MicroRNA Analysis?
Thanks to high-throughput sequencing technologies, researchers can now obtain vast amounts of miRNA sequencing data. This data provides valuable insights into the complex world of gene regulation. However, analysing miRNA sequencing data is no easy task. The sheer volume of data, coupled with the inherent intricacies of miRNA biology, necessitates the use of sophisticated computational tools and techniques. This is where bioinformatic analysis comes in. By employing a wide range of computational algorithms and statistical methods, bioinformaticians can uncover hidden patterns and unveil the secrets encoded within miRNA sequencing data.
One of the main goals of microRNA sequencing data analysis is to identify differentially expressed miRNAs. These are miRNAs that exhibit statistically significant changes in expression levels between different biological conditions or disease states. Bioinformatic analysis of miRNA sequencing data makes it possible to pinpoint these differentially expressed miRNAs and quantify any change in abundance. In turn, this enables researchers to gain insights into the underlying regulatory mechanisms that govern various biological processes. Additionally, miRNA sequencing data analysis allows for the prediction of miRNA targets and functional annotation, shedding light on the specific genes and pathways influenced by RNA molecules.
In short, bioinformatic analysis plays a pivotal role in unravelling the mysteries concealed within microRNA sequencing data. It enables researchers to decipher the complex regulatory networks governed by miRNAs and provides a deeper understanding of their functional implications in health and disease.
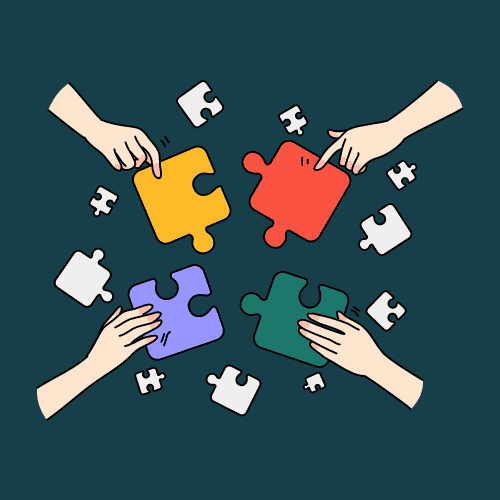
Key Steps in Bioinformatic Analysis of MicroRNA Sequencing Data
Analysing microRNA sequencing data involves a series of steps that reveal the information hidden within the RNA molecules. Each step is crucial for obtaining reliable and meaningful results. Let’s take a look at each of the steps below.
Pre-processing and Quality Control of MicroRNA Sequencing Data
The first step in miRNA sequencing data analysis is pre-processing and quality control. Raw sequencing data often contains artifacts, such as sequencing errors and adapter contamination, which can affect downstream analysis. Therefore, it is essential to perform quality control to ensure the reliability of the data.
During pre-processing, several steps are typically performed, including adapter removal, trimming of low-quality bases, and filtering out reads of insufficient length. This helps to eliminate artifacts and retain only high-quality sequences for further analysis.
Quality control measures, such as examining sequence quality scores and assessing the presence of overrepresented sequences, further ensure the integrity of the data. It is important to note that the method by which samples were processed and sequenced can influence the appropriate data processing and quality control steps. These measures help to ensure accurate downstream analysis and interpretation of results.
Mapping and Alignment of MicroRNA Sequencing Data
After pre-processing and quality control, the next step is mapping and alignment of miRNA sequencing data. This step involves aligning the processed reads to a reference genome or miRNA database to determine the origin and abundance of each sequence.
Alignment of miRNA sequencing data is a critical step as it allows researchers to associate each sequence with its respective miRNA or genomic location. This information serves as a foundation for downstream analysis, such as differential expression analysis and target prediction.
Differential Expression Analysis of MicroRNA Sequencing Data
Differential expression analysis is a key component of miRNA sequencing data analysis, enabling researchers to identify miRNAs that exhibit significant changes in expression levels between different biological conditions or disease states.
The output of differential expression analysis typically includes a list of differentially expressed miRNAs, along with statistical measures of significance, such as p-values and fold changes in abundance values. These results provide valuable insights into the miRNAs that play a vital role in the biological processes being investigated.
Functional Annotation and Pathway Analysis of Differentially Expressed MicroRNAs
Once the differentially expressed miRNAs have been identified, a further analysis step can be to unravel any functional implications. Functional annotation and pathway analysis allow researchers to gain insights into the specific genes and pathways influenced by these miRNAs.
Functional annotation involves associating the differentially expressed miRNAs with their putative target genes. The aim of pathway analysis is then to identify the biological pathways and processes that are significantly enriched with differentially expressed miRNA target genes.
Functional annotation and pathway analysis provide a comprehensive understanding of the biological processes influenced by differentially expressed miRNAs. This knowledge is crucial for elucidating the underlying molecular mechanisms and developing potential therapeutic interventions.
Integration of MicroRNA Sequencing Data with Other Omics Data
Integrating miRNA sequencing data with other omics data can provide a more holistic view of gene regulation and functional implications.
For example, integrating miRNA sequencing data with mRNA expression data allows researchers to identify miRNA-mRNA regulatory pairs. Identifying those regulatory pairs then sheds light on the intricate crosstalk between miRNAs and their target genes.
Similarly, integration of miRNA sequencing data with DNA methylation data provides insights into the epigenetic regulation of miRNAs and their target genes. DNA methylation can modulate miRNA expression, and as a result, influence gene expression and cellular phenotypes.
By integrating miRNA sequencing data with other omics data, researchers can unravel the complex interactions and regulatory networks that govern gene expression. This paves the way for a deeper understanding of biological processes and disease mechanisms.
Challenges and Limitations in Bioinformatic Analysis of MicroRNA Sequencing Data
While bioinformatic analysis has revolutionised our understanding of miRNA sequencing data, it is not without its challenges and limitations. Several factors can impact the accuracy and reliability of the results obtained through bioinformatic analysis.
One of the main challenges is the choice of computational algorithms and statistical methods. The selection of appropriate tools and techniques depends on various factors, such as sample preparation, sequencing platform, the characteristics of the data, the research question, and the available computational resources. However, the performance and accuracy of different algorithms can vary, leading to discrepancies in the results.
The inherent biases and technical artifacts associated with miRNA sequencing data also present challenges. These biases can arise from sample preparation, sequencing protocols, and data processing steps. It is important to account for these biases during data analysis in order to ensure accurate interpretation of the results.
What’s more, miRNA sequencing data analysis often involves large datasets, which can be challenging. For instance, analysing large miRNA sequencing datasets requires substantial computational resources and expertise. Also, the analysis pipelines can be computationally intensive, requiring access to high-performance computing infrastructure.
Furthermore, the interpretation of miRNA sequencing data analysis results requires biological knowledge and expertise. Understanding the functional implications of differentially expressed miRNAs and their target genes requires a comprehensive understanding of molecular biology and relevant biological processes.

Overcoming the Challenges and Limitations of Bioinformatic Analysis of MicroRNA Sequencing Data
The good news is, all of the challenges above can be overcome by outsourcing the analysis to a reputable bioinformatics provider. Established bioinformatics providers have the experience and expertise to select the algorithms, tools and techniques which will be best for answering your research question, while also accounting for the characteristics of the data to be analysed.
Their experience also means they will be adept at accounting for and addressing the biases associated with miRNA sequencing data. Also, bioinformatics providers have the computational resources necessary for handling and analysing microRNA sequencing data.
Perhaps most important of all, established bioinformatics providers have the biological knowledge and experience required to fully understand and interpret miRNA sequencing data analysis results. This enables them to pinpoint the results that are meaningful to your research question, and draw conclusions from them.
If you need bioinformatic analysis of microRNA sequencing data, Fios Genomics can help. We have been providing our bioinformatic analysis services for over 15 years, so you can rely on our experience and expertise. We are known for quality and speed and have a 95% repeat business rate. If you have a question about microRNA sequencing data or wish to discuss an analysis project, contact us and we will be happy to help!
Author: Breige McBride, Content and Social Media Manager, Fios Genomics
Reviewed by Fios Genomics Bioinformatics Experts to ensure accuracy
More from Fios Genomics
Common Steps in Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data Analysis
RNA-Seq or Microarray: Which Sequencing Technology is Best for Your Study?